Design thinking isn’t just a buzzword, it’s a powerful, human-centered approach to problem-solving that transforms ideas into meaningful outcomes. Professionals in tech, business, education, and design increasingly rely on this structured process to solve real-world challenges creatively and effectively.
At its core, design thinking prioritizes empathy, experimentation, and iteration. It empowers teams to develop solutions that truly resonate with user needs. Whether you’re developing a product or improving a service, this methodology can lead to innovation that makes a difference.
Understanding and applying the 5 steps in design thinking, individuals and organizations can unlock their creative potential. These steps guide you from problem discovery to successful implementation.
What Are the 5 Steps in Design Thinking?
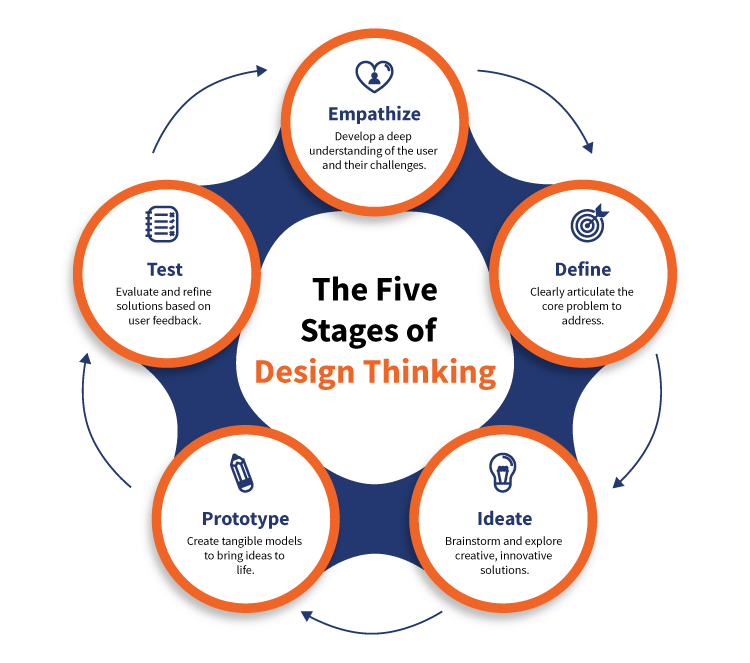
The 5 steps in design thinking are a structured framework used to solve complex problems with a user-centric approach. These steps include Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, and Test.
Each step builds upon the last to ensure the solution addresses the real needs of the end user. This process is iterative meaning you can revisit earlier stages as you learn more.
Design thinking doesn’t follow a strict linear path. Instead, it’s flexible, allowing room for innovation through continuous feedback and refinement. These five stages serve as a practical roadmap for creating effective and innovative solutions grounded in empathy and creativity.
5 Design Thinking Stages at a Glance
Understanding the 5 steps in design thinking helps professionals approach challenges with confidence and clarity. Let’s take a quick look at each stage and why it’s crucial:
1. Empathize
The journey starts with building empathy. Designers seek to understand users by observing behaviors, conducting interviews, and immersing themselves in the users’ experiences. This step ensures solutions are based on real human needs, not assumptions.
2. Define
Insights gathered during empathy lead to problem definition. Here, teams create clear problem statements by analyzing patterns and identifying core user needs. A well-defined problem is essential to crafting an effective solution.
3. Ideate
Once the problem is clear, brainstorming begins. The ideation phase encourages creativity, allowing teams to explore a wide range of potential solutions. Tools like mind mapping and sketching promote innovation and collaboration.
4. Prototype
This stage turns ideas into tangible models. Prototypes are low-fidelity versions of the product or service that help teams visualize and refine their concepts. It’s about building to think and learn.
5. Test
Testing involves presenting prototypes to users for feedback. This helps identify strengths and weaknesses, guiding refinements. Testing may lead back to previous steps to improve the solution further.
Importance of These Stages
These five stages promote deep understanding, targeted problem-solving, and continual improvement. They empower businesses to reduce risk, boost user satisfaction, and innovate responsibly. With each step, teams get closer to delivering meaningful, user-centered solutions.
Deep Dive Into Each Step
Let’s explore each of the 5 steps in design thinking in depth, highlighting essential elements that bring this methodology to life. These elements help teams harness creativity, uncover hidden needs, and build thoughtful solutions. For top-tier support in implementing these principles, many turn to Musemind UX Design Experts in Munich for professional guidance and project execution.
Empathy Research Techniques
Empathy requires connecting deeply with users. Techniques like shadowing, in-depth interviews, and diary studies help uncover not just what users do but why they do it. This emotional insight becomes the foundation of great design.
Empathy research also involves eliminating bias by engaging a diverse user base. The more perspectives gathered, the more inclusive the final design will be.
Crafting a Clear Problem Statement
After collecting insights, teams synthesize their findings into a meaningful problem statement. This step clarifies the challenge in user-centric language.
A good problem statement avoids broad generalizations and focuses on specific needs. It aligns the team around a shared goal and sets the direction for ideation.
Brainstorming Without Limits
During ideation, quantity leads to quality. Teams are encouraged to think big, suspend judgment, and build upon each other’s ideas.
This creative freedom often leads to unexpected and powerful innovations. Tools like SCAMPER, Crazy 8s, and brainwriting are frequently used to spark ideas.
Building Prototypes That Speak
Prototypes can be anything from a sketch to an interactive digital model. Their purpose is to communicate ideas clearly and test feasibility early.
Prototyping helps minimize wasted resources. By building something quickly and cheaply, teams can test assumptions before heavy investment.
Testing with Purpose
Testing is more than just usability, it’s about learning. Observing users interact with prototypes reveals gaps, frustrations, and missed opportunities.
Constructive feedback should be encouraged and recorded carefully. Every round of testing brings a better version of the product closer to reality.
Iterating Based on Insights
Design thinking isn’t a one-time pass. Iteration is key. Feedback loops allow teams to revisit earlier steps to refine the solution.
Whether it’s redefining the problem or adjusting the prototype, iteration ensures the final product truly resonates with users.
Collaboration Across Teams
Cross-functional collaboration amplifies the power of design thinking. Involving designers, developers, marketers, and stakeholders ensures diverse perspectives are considered.
This teamwork leads to solutions that are not only desirable for users but also feasible and viable for the business.
Real-World Applications
The 5 steps in design thinking can be applied to almost any problem-solving scenario. Here’s a quick guideline to help you apply these steps effectively in your context:
1. Identify a Real Problem:
Start with something meaningful to solve a customer complaint, a business inefficiency, or a product gap.
2. Conduct Empathy Research:
Talk to real users. Use interviews, observations, and surveys to understand their frustrations and goals.
3. Define the Challenge:
Summarize your findings in a problem statement that reflects user needs not company goals.
4. Generate Ideas:
Gather your team and brainstorm openly. Use prompts or frameworks to push creative boundaries.
5. Build & Test Prototypes:
Sketch ideas, make mockups, and test them with users. Collect feedback, refine, and improve.
Final Thought
The 5 steps in design thinking provide a proven framework for tackling complex challenges with empathy, creativity, and confidence. From uncovering real user needs to testing impactful solutions, this process ensures innovation stays grounded in human experience.
Individuals and organizations can unlock the full potential of design thinking to drive innovation and long-term success.